Síntomas y tratamiento de la infección del tracto urinario (ITU)
Encuentre un urólogoUna infección de las vías urinarias (IVU) es una infección bacteriana en cualquier parte de las vías urinarias. This includes your kidneys, bladder, the tubes that carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder (ureters), and the tube that connects your bladder to the outside of your body (urethra).
Las infecciones de las vías urinarias ocurren con mayor frecuencia en la vejiga y la uretra. Por lo general, son dolorosas y molestas, aunque no son dañinas a menos que la infección se propague a los riñones. Las mujeres son más propensas a desarrollar infecciones urinarias que los hombres, y entre el 40 % y el 60 % de las mujeres informaron haber tenido una IVU al menos una vez en la vida.
Get relief from a UTI with a video visit with your virtual primary care or in-person provider. Or visit an urgent care center to see an Aurora Health Care urology expert.
Need care now? Try telehealth
El Symptom Checker puede ayudarlo a encontrar el tipo de atención adecuado según sus síntomas. From 24/7 urgent care video visits to e-visits, we’ll recommend the best visit for you. Try Symptom Checker in LiveWell.
How does a UTI make you feel?
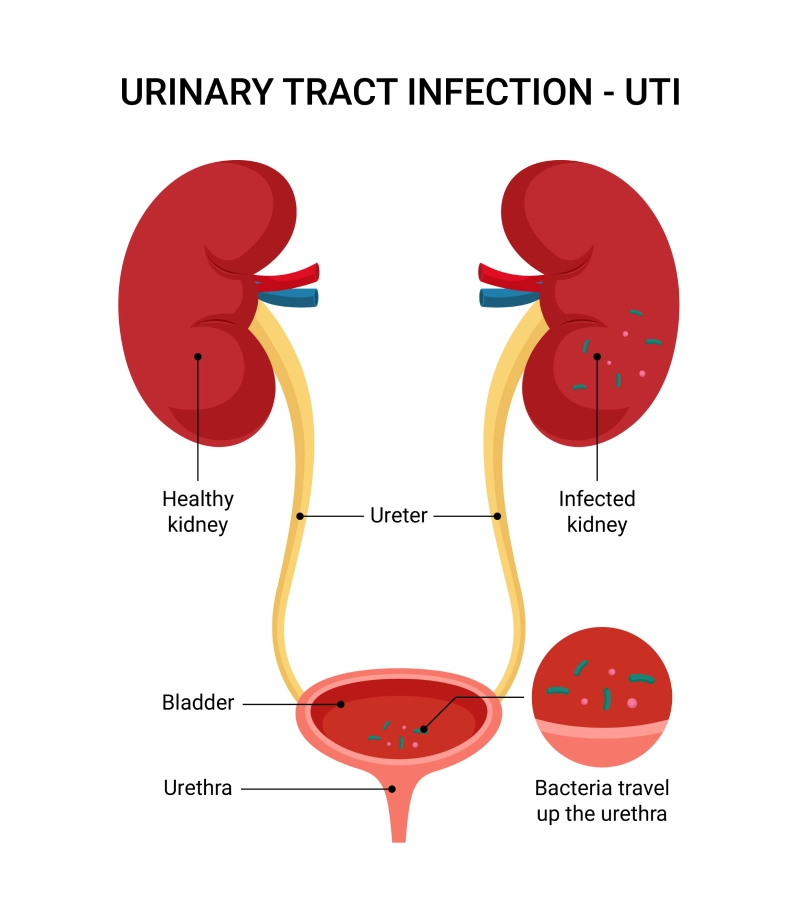
When you have a urinary tract infection (UTI), bacteria may travel from the urethra to the bladder and kidneys, leading to an infected kidney or bladder.
A UTI can be extremely uncomfortable, and how it makes you feel depends on the severity and location of the infection. Pain or burning while going to the bathroom is common if you have a UTI. You may feel like you need to urinate a lot but may have very little urine come out.
Your urine may look cloudy or dark and have a strong smell. Low back pain, chills, and fatigue are also common if you have a UTI.
Síntomas de una infección de las vías urinarias (IVU)
If you have a UTI, symptoms may include:
- Sensación de ardor al orinar
- Orina turbia
- Sentir una necesidad imperiosa de orinar que no desaparece incluso después de orinar
- Frequent urination, often in tiny amounts
- Orina de olor fuerte
- Dolor pélvico
- Pink, red, or brown urine, which is a sign that you have blood in your urine (hematuria)
- Dolor rectal en hombres
Tipos de infección de las vías urinarias (IVU)
Depending on where in your urinary tract an infection develops, your potential UTI symptoms may differ.
UTI in the bladder (cystitis)
Also known as a bladder infection, you may experience an intense urge to urinate frequently. You may also notice pain with urination, cloudy urine, and discomfort in your lower abdomen.
UTI in a kidney (pyelonephritis)
Esto generalmente ocurre cuando las bacterias de una infección de la vejiga se propagan a los riñones. You may experience more severe UTI symptoms, such as back pain, fever, chills, and nausea.
UTI in the urethra (urethritis)
Esto ocurre cuando la infección conduce a la inflamación de la uretra. Puede experimentar secreción y dolor al orinar.
Póngase en contacto con su médico si cree que puede estar experimentando algún síntoma de IVU.
Is a UTI a STI?
Although UTI symptoms may be similar to some symptoms of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), UTIs aren't considered to be STIs.
STIs are infections transmitted through sexual contact and are caused by specific bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Whereas the bacteria that causes UTIs is usually from the gastrointestinal tract, such as E. coli.
Although UTIs and STIs are different, some UTI symptoms, such as pain during urination, may overlap with STI symptoms. It’s important to see your doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causas de la infección de las vías urinarias (IVU)
A UTI typically occurs when bacteria enter the urinary tract. E. coli bacteria, found in the large intestine, can move easily from the anus into the urethra, making it responsible for 90% of bladder infections.
Due to human anatomy, females are more likely to develop a UTI because they have a shorter urethra than males. This gives bacteria easier access to the urinary tract, especially during sexual activity.
Women who are postmenopausal are more likely to experience urinary tract infections (UTIs) due to lower estrogen levels. During menopause, estrogen levels decline, which affects the lining of the urinary tract. Estrogen helps maintain the health of the urethra and bladder, which helps reduce the risk of bacterial infections. When estrogen levels drop, the lining becomes thinner and more vulnerable to infections.
Diagnóstico y tratamiento de las infecciones de las vías urinarias (IVU)
Your Aurora urologist will talk with you about your potential UTI symptoms and take a urine sample to test for bacteria, white blood cells or blood. If you have frequent UTIs, your doctor might recommend additional imaging tests or inserting a scope into your bladder to check for other causes.
Una vez que haya recibido un diagnóstico, el médico trabajará con usted para decidir el tratamiento adecuado para satisfacer sus necesidades. La mayoría de las infecciones de las vías urinarias se pueden curar con antibióticos. Si tiene infecciones de las vías urinarias con frecuencia, el médico podría recomendar un ciclo más prolongado de antibióticos o, si es mujer, antibióticos de dosis única después de las relaciones sexuales o la terapia de estrógeno vaginal.
You may feel relief of UTI symptoms after 24-48 hours of taking antibiotics, but it typically takes up to seven days for the bacteria to clear out of the urinary system. El tipo y la duración del tratamiento dependen de las bacterias que se encuentren en la orina y de su estado de salud actual.
While it’s possible for a UTI to resolve on its own, most of the time it doesn’t and can get worse without proper treatment. Si la infección es grave, podría tener que permanecer en el hospital para recibir antibióticos por vía intravenosa y atención las 24 horas para prevenir el daño renal.
Prevención de la infección del tracto urinario (IVU)
The following tips can help you prevent getting a UTI in the future:
- Urinate before and after sexual activity.
- Wipe in a front-to-back motion after urination or a bowel movement.
- Aumente la ingesta de líquidos, especialmente agua.
- Tome duchas en lugar de baños.
- Avoid using scented feminine hygiene products in the genital area.
Some studies have shown that cranberry-based products may be effective in fighting urinary tract infections, although results are inconclusive. Consuming unsweetened cranberry juice, cranberry supplements, or dried cranberries may help prevent bacteria from sticking to the walls of the urinary tract.
Reciba atención
Le ayudamos a vivir bien. Podemos ayudarle en persona o en línea.