Síntomas y tratamiento de la osteoporosis
Solicite una citaSus huesos están formados por tejido vivo y en crecimiento. A medida que muere el tejido óseo antiguo, el cuerpo produce constantemente tejido óseo nuevo y fuerte. With osteoporosis, old bone is not replaced by new bone fast enough, causing a decrease in bone mass and bone density.
Over time, your bones become weaker and thinner and may fracture easily – even from bending, coughing, lifting light objects or a minor fall. Osteoporosis is called a silent disease because most people who have it don’t notice osteoporosis symptoms.
Síntomas de la osteoporosis
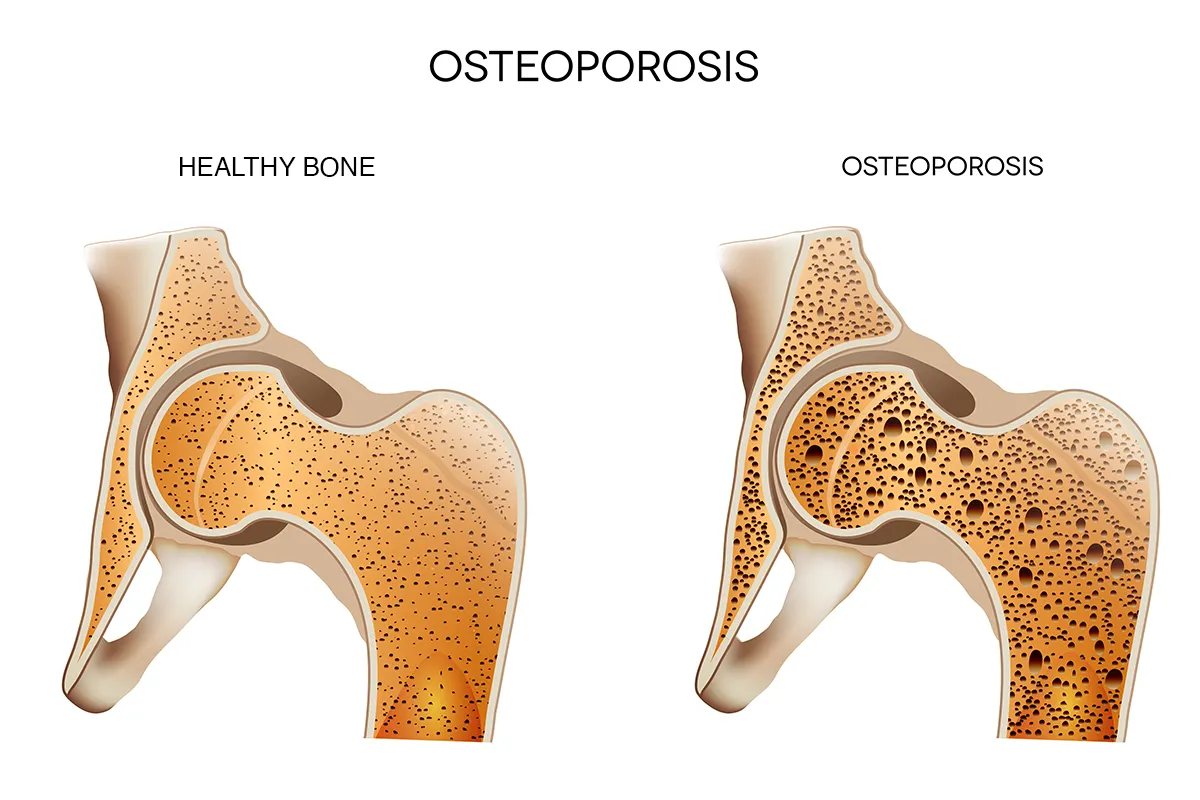
Osteoporosis makes bones gradually become less dense and more fragile. People with osteoporosis have a higher risk of broken bones, especially hips, wrists and vertebrae.
Los síntomas de la osteoporosis pueden incluir:
- Una postura encorvada (cifosis) al estar sentado o de pie
- Pérdida de altura con el tiempo
- Collapsed or fractured vertebrae
- Huesos que se fracturan con facilidad
- Dolor de espalda
You may not notice any osteoporosis symptoms until you already have significant bone loss.
Las cuatro etapas de la osteoporosis
Osteoporosis develops gradually, and it’s often not diagnosed until you break a bone.
Estadio 1: Durante las edades de 20 a 40 años aproximadamente, los huesos se degradan al mismo ritmo que se forma tejido nuevo. Esta se considera la primera etapa de la osteoporosis porque el crecimiento óseo ya no es más rápido que la pérdida ósea, como lo es desde el nacimiento hasta la adolescencia. There are no symptoms at this stage.
Estadio 2: En esta etapa, la pérdida ósea comienza a superar el crecimiento óseo. Si sufre una lesión o se somete a una prueba de densidad ósea por otro motivo, es posible que le diagnostiquen osteopenia o pérdida ósea leve.
Estadio 3: Si llega a esta etapa, oficialmente tiene osteoporosis. You still might not notice any osteoporosis symptoms, but you’ll be at increased risk for breaks and fractures – even from simple injuries like hitting your leg against a door. Symptoms at this stage may include having brittle nails, weakness in your hands, receding gums or tooth loss.
Estadio 4: Esta es la forma más grave de osteoporosis. Softer and weaker bones may show in the form of spinal deformities such as a bent-over appearance called kyphosis and pain with everyday activities. At this stage most people have had one or more broken bones because of osteoporosis.
What are the main causes of osteoporosis?
The main causes of osteoporosis are loss of bone mass and bone density. Your bones become thinner and weaker. The wrists, hips and vertebrae in the spine are the bones most affected by osteoporosis.
Your chances of getting osteoporosis may be increased by several risk factors, such as:
- Género: Women are at greater risk for osteoporosis because they usually have thinner, less dense bones than men. Men are also at risk but don't usually get osteoporosis until after age 70.
- Edad: Bone growth slows as you get older.
- Origen étnico: Osteoporosis is most common in non-Hispanic White people and in Asian women.
- Antecedentes familiares: If a parent has a history of hip fracture or osteoporosis.
- Hormonas: Low levels of testosterone in men and low levels of estrogen in women.
- Dieta: Excessive dieting for weight loss or consuming a diet low in calcium, protein or vitamin D.
- Ciertos tipos de afecciones médicas: Endocrine and hormonal diseases, gastrointestinal diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, HIV/AIDS and anorexia nervosa.
- Actividad física: Lack of exercise, or sedentary lifestyle.
- Abuso del alcohol: Chronic frequent drinking.
- Fumar cigarrillos: Smoking is linked to increased risk of osteoporosis.
Diagnóstico de osteoporosis
Doctors usually diagnose osteoporosis during a routine screening for the disease. Women may start screening at age 65 or sooner if they have a high risk of osteoporosis. Cuando visite a su médico, recuerde informar:
- Cualquier fractura previa
- Your regular habits of diet, exercise and alcohol use
- Your smoking history
- Afecciones médicas y medicamentos actuales o pasados
- Sus antecedentes familiares de osteoporosis y fracturas óseas
- Para las mujeres, su historial menstrual
Su médico puede realizar un examen físico para controlar lo siguiente:
- Pérdida de altura y peso
- Cambios en la postura
- Equilibrio y marcha (la forma de caminar)
Las pruebas podrían incluir:
- Análisis de sangre
- Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) to measure bone mass and thickness
- Una radiografía, una resonancia magnética o una tomografía computarizada para mostrar las fracturas nuevas o existentes
Tratamiento de la osteoporosis
The goals for treating osteoporosis are to slow or stop bone loss and prevent bone fractures. Treatments range from changes to your daily habits to minimize bone loss in early stages of osteoporosis, to spinal surgery to treat pain and repair bone damage in advanced stages.
Self-care for osteoporosis
There are some things you can do yourself to protect your bone health, including:
- Doing weight-bearing exercises such as walking and lifting weights to increase strength, muscle mass, coordination and balance
- Limiting use of alcohol
- No fumar
- Eating a nutritious diet rich in calcium, vitamin D and protein
Tratamiento no quirúrgico para la osteoporosis
When possible, your doctor will start with nonsurgical osteoporosis treatments such as:
- Fall prevention education to help avoid fractures
- Suplementos de calcio y vitamina D
- Medicamentos, si se recetan, para el dolor o para tratar la osteoporosis
- Fisioterapia
- Asesoramiento para bajar de peso
Tratamiento quirúrgico para la osteoporosis
More serious osteoporosis symptoms may require osteoporosis treatments like the following:
- Cirugía de fusión espinal: Two vertebrae are permanently connected to reduce pain, increase the stability of the spine and stop the formation of bone spurs.
- Bloqueo del nervio espinal: Your doctor injects an anesthetic drug near or directly into your spinal nerve. Spinal nerve blocks may be used for pain relief or as a diagnostic tool to find what’s causing your pain.
- Estabilización de la columna: Your doctor implants rods, screws or locking plates in the bones of your spine. An orthotic vest or brace may be used for less severe fractures.
- Vertebroplastia: Your doctor injects a medical-grade substance called bone cement, which holds the spine bones in their proper position to reduce pain and bone deformity.
- Cifoplastia: primero se inserta un globo en el área afectada para descomprimir la columna y permitirle recuperar la altura perdida. Luego, el médico inyecta cemento óseo para estabilizar las vértebras.
Complicaciones de la osteoporosis
En etapas avanzadas, la osteoporosis puede causar otros padecimientos de salud u ocurrir junto con otras afecciones, entre ellas:
- Cervical spinal stenosis and myelopathy (cervical spondylotic myelopathy): estrechamiento del conducto vertebral en el área del cuello, que puede hacer que la médula espinal se comprima o se dañe. Symptoms may include pain, tingling, balance problems, numbness, muscle weakness and dizziness.
- Fractura por compresión de la columna: A break or rupture in the bones of the spine (also called collapsed vertebrae). El signo más común es el dolor de espalda intenso.
- Tetania hipocalcémica: When extremely low blood levels of calcium cause involuntary muscle contractions.
- Radiculopatía: Pressure on a nerve root that causes pain, numbness or weakness. May also cause difficulty controlling specific muscles.
Encuentre atención para la columna vertebral cerca de usted
Cuando tiene osteoporosis, estamos aquí para que le resulte más fácil volver a las cosas que más le importan. With your own care coordinator, you’ll be connected to an integrated team of specialists all working together on your personalized osteoporosis treatment plan. Learn more about our spine services locations.
Aurora St. Luke’s Medical Center
¿Le preocupa el dolor de espalda y cuello?
El dolor de espalda y cuello puede interrumpir incluso las cosas más simples de la vida e indicar un problema grave. Nuestro cuestionario sobre el dolor de espalda y cuello ayuda a evaluar el funcionamiento de la columna vertebral, los síntomas del dolor y los factores de riesgo, y le da una idea de qué hacer a continuación según sus resultados.
Reciba atención
Le ayudamos a vivir bien. Podemos ayudarle en persona o en línea.